THANK YOU FOR VIEW OUR BLOG...
Wednesday, 9 October 2013
FUNCTIONS
BUS TOPOLOGY
vIt is a multipoint topology.
vOne long cable acts as a backbone to link all the
devices in the network.
STAR
TOPOLOGY
vEach device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller.
vIt does not allow direct
traffic between devices.
ring
TOPOLOGY
vEach device has a directed point-to-point line
configuration.
vMessage will be passed to each device until it
reach the destination.
mesh
TOPOLOGY
vA mesh topology provides redundant communication paths between some or all devices.
vTwo categories of Mesh Topology :
Ø Full Mesh Topology :Normally use went we found a compelling
reason to inner connect multiple location for direct connectivity to every other
location.
Ø Partial Mesh Topology : At least one device maintain multiple connection to the other
devices, however other connection do not have to be maintain directly to every
other devices.
tree
TOPOLOGY
vA tree topology integrates the star & bus topologies in a hybrid approach to improve network scalability.
hybrid
TOPOLOGY
vThe combination of two or more topologies.
Monday, 23 September 2013
PROS & CONS
TOPOLOGY
|
PROS
|
CONS
|
|
Bus
|
Use of cable is economical.
|
Network can slow down
in heavy traffic.
|
|
Media is inexpensive & easy to work with.
|
Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable.
|
||
System is simple & reliable.
|
Problem are difficult to
isolate.
|
||
Bus is easy to extends.
|
Terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable.
|
||
Star
|
Failure of one
computer does not
affect the rest of the network.
|
If the centralized
point fails, the network fails.
|
|
Modifying system and adding new computers is
easy.
|
Costs
are usually higher
than with bus or ring networks.
|
||
Centralized monitoring
& management are possible.
|
|||
Ring
|
System provides equal access for all computers.
|
Failure of one computer can impact the rest of the network.
|
|
Performance is even despite many
user.
|
Problem are hard to isolate.
|
||
Unmanageable in a large network.
|
|||
Mesh
|
System provides increased
redundancy & reliability as well as ease of
troubleshooting.
|
System is expensive to install because it uses a lot of cabling.
|
|
Tree
|
Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
|
Overall length of each segments is limited by the type of
cabling used.
|
|
Supported by several hardware &
software venders.
|
If the backbone line breaks, the entire segments goes down.
|
||
More difficult to configure & wire than
other topologies.
|
|||
CHARACTERISTIC
TOPOLOGY
|
CABLE
|
SPEED
|
PROTOCOL
|
Bus, Star, Tree
|
Twisted Pair,
Coaxial, Fiber
|
10 Mbps
|
Ethernet
|
Star
|
Twisted Pair,
Fiber
|
100 Mbps
|
Fast Ethernet
|
Linear or Star
|
Twisted Pair
|
23 Mbps
|
LocalTalk
|
Star-Wired Ring
|
Twisted Pair
|
4 Mbps - 16
Mbps
|
Token Ring
|
Dual ring
|
Fiber
|
100 Mbps
|
FDDI
|
Bus, Star, Tree
|
Twisted Pair,
Fiber
|
155 - 2488 Mbps
|
ATM
|
Sunday, 22 September 2013
INTRODUCTION
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
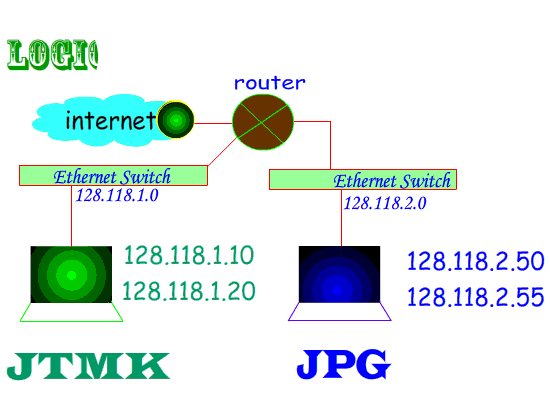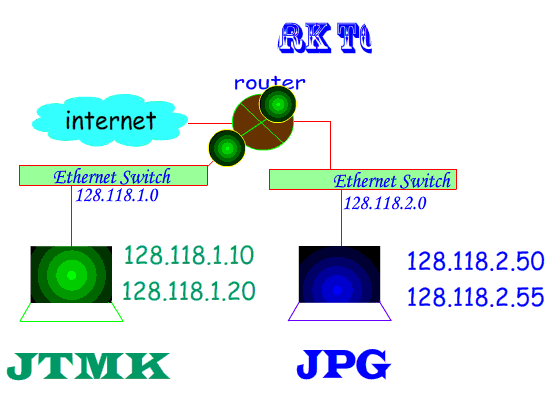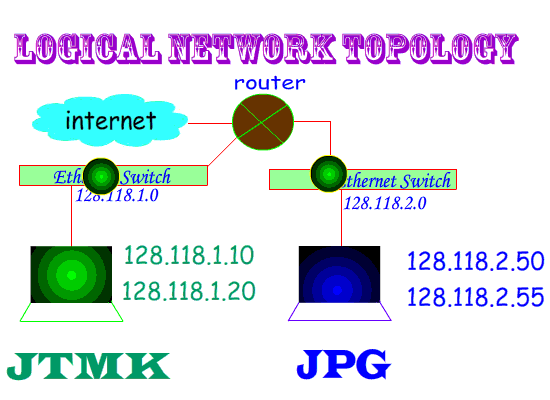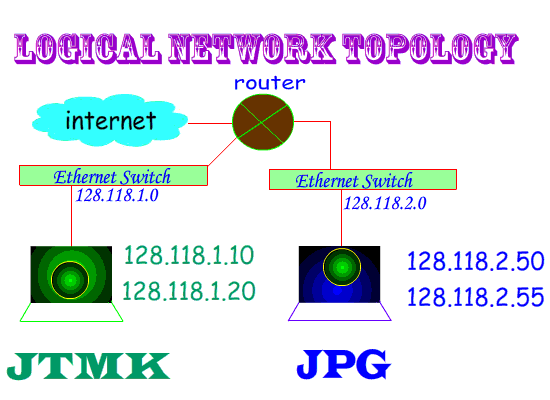
Two Categories of Network Topology :
Physical :- Topology map recorded each host is located, wiring is installed and the locations of the networking devices that connect the hosts.
Logical :- Host names, addresses, group information & applications can be recorded on the logical pathway a signal follows as it passes among the network nodes.
Logical :- Host names, addresses, group information & applications can be recorded on the logical pathway a signal follows as it passes among the network nodes.
Friday, 20 September 2013
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)